Carotid triangle contents
The carotid triangle is a paired triangular space at the anterior portion of the neck region and carotid triangle contents following structure including; (@ VANCaL)
- Veins
- Arteries
- Nerves
- Carotid sheath and its contents
- Lymph nodes
- Veins: including following (@ LiP FIj)
- The lingual vein which usually terminates in internal jugular veins
- The pharyngeal vein which usually ends in internal jugular veins
- Common Facial vein draining into an internal jugular vein around the neck region
- Internal jugular vein
- Arteries: including following (@ 3C with its branches)
- A common carotid artery with carotid sinus and carotid body at its termination at the carotid triangle in the neck region
- Internal carotid artery
- An external carotid artery with its branches such as superior thyroid, lingual, facial, ascending pharyngeal, and occipital arteries.
- Nerves: Including the following (@ VAL HS)
- Vagus nerve running vertically downwards
- Spinal accessory nerve running backward over the internal jugular vein
- Superior laryngeal branch of the vagus, dividing into external and internal laryngeal nerves.
- Hypoglossal nerve running forwards over the external and internal carotid arteries
- Sympathetic chain running vertically downwards posterior to the carotid sheath
- Carotid sheath with its contents such as an internal jugular vein, common carotid artery, vagus nerve.
- Lymph nodes: Deep cervical lymph nodes
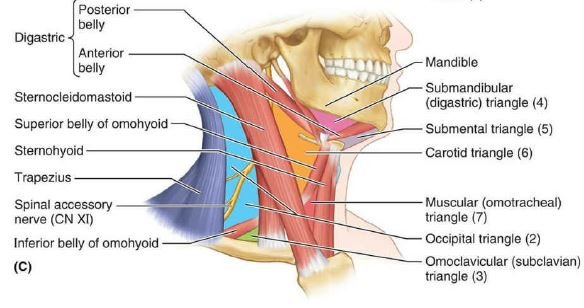
Boundaries of the carotid triangle
The boundaries of a carotid triangle are following;
- Anterosuperiorly: the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, stylohyoid muscle.
- Anteroinferiorly: the superior belly of the omohyoid muscle
- Posteriorly: anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Roof:
The carotid triangle roof contains the following structures;
-
- Skin
- Superficial fascia containing
- Platysma
- Cervical branch of the facial nerve
- The transverse cutaneous nerve of the neck
- Investing layer of deep cervical fascia
- Floor
The floor of a carotid triangle formed by the following structures;
-
- Middle constrictor of the pharynx
- Inferior constrictor of the pharynx
- Thyrohyoid membrane
Applied anatomy
- Carotid sinus syndrome: The carotid sinus is richly supplied by nerves. In some conditions, the sinus may be hypersensitive and sudden rotation of the head may cause slowing of the heart. This condition is called carotid sinus syndrome.
- Supraventricular tachycardia: It may be controlled by carotid sinus massage due to inhibitory effects of the vagus nerve on the heart.