Overview of Zopiclone
Zopiclone is an orally effective cyclopyrrolone derivative & is used for the short-term treatment of conditions called insomnia. It produces near-normal sleep such as Benzodiazepines (BZDs) drugs.
Mechanism of action
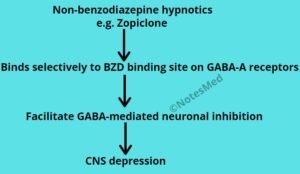
Zopiclone is the non-benzodiazepine hypnotics that bind selectively to BZD binding site on GABAa receptors and facilitate GABA-mediated neuronal inhibition (due to the enhanced membrane hyperpolarization) and finally produce CNS depression.
Uses of Zopiclone
- Oral short-term management of insomnia
- Adult: 7.5 mg at bedtime
- Elderly: Initially, 3.75 mg at bedtime.
- Renal impairment: initiate at 3.75 mg at bedtime
- Hepatic impairment: Mild to moderate conditions-initially 3.75 mg at bedtime.
- Severe hepatic insufficiency: 3.75 mg at night.
- Sedative and hypnotic
Contraindications
- Severe hepatic impairment
- Myasthenia gravis
- Respiratory failure
- Severe sleep apnea syndrome
- Pregnancy and lactation
Special precautions
- Hepatic and renal insufficiency
- Elderly
- Psychiatric disorders
- History of drug abuse
Adverse effects
- CNS depression ranging from drowsiness to coma depending on the ingested amount.
- In mild cases:
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Lethargy
- Headache
- GI disturbances
- Metallic taste or bitter taste
- Irritability
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Urticaria
- Rashes
- Serious case:
- Ataxia
- Aggressiveness
- Hypotonia
- Hypotension
- Respiratory depression
- Coma
When you and your family use this drug than may chance to developed various side effects in your body then consult your doctors. There are the following management methods are briefly explained which are done by your doctor.
Management of side effects
The treatment is symptomatic and supportive with close monitoring of respiratory and cardiovascular functions. Gastric lavage is only of value if performed within one hour after ingestion. Haemodialysis is unlikely to be useful and flumazenil may be a useful antidote in severe CNS depression.
Interactions
- Reduced hypnotic effect with drug phenytoin and carbamazepine.
- Decreased zopiclone concentration with rifampicin
- Increased zopiclone concentration with CYP3A4 inhibitors (such as; erythromycin, clarithromycin, ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir, etc.)
- Increased CNS depressant effects with alcohol and other CNS depressant agents.