Overview of Toxoplasma gondii
Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular coccidian parasite, It was first described in 1908 by Nicolle and Manceaux in a small rodent called gondii in North American.
It is widely distributed in man and animals. The term Toxoplasma arises from a Greek word, Toxon= arc or brow referring to the curved shape, plasma means form. That means small crescent form tachyzoite is called trophozoites.
Morphology of Toxoplasma gondii
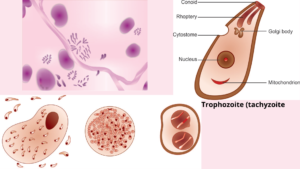
There are occur in three forms, they are
- Trophozoites or tachyzoites
- Tissue cyst
- Oocyst
All three forms are infective to humans. Trophozoites and tissue cyst stages represent asexual called schizogony, while the Oocyst is formed by sexual reproduction called gametogony or sporogony.
Trophozoites
The trophozoite is crescent-shaped, with one extremity (end) is pointed and the other end rounded. Its length about 3-7um.
The nucleus is ovoid and situated at the blunt end of parasites and stains well with Giemsa stain, the cytoplasm appearing azure blue and the nucleus, red.
In acute infection, Pseudocyst or colony is a proliferating trophozoite within host cell may appear rounded and enclosed by a host cell membrane and Tachyzoites is rapidly proliferating trophozoites in acute infection.
Tissue cyst
Tissue cyst is a resting form of the parasite and found during the chronic stage of infection and most commonly present in the brain and also found in skeletal muscles, and other various organs.
A cyst is round or oval,10-20um in size and it is a slowly multiplying parasite within the cyst wall is called bradyzoites.
Oocyst
Oocyst is developed only in definitive hosts in the intestine of Cats and other feline but not in humans being. It is an oval, about 10-12um in diameter, and surrounded by a thick resistant wall on this parasites.
It is formed by sexual reproduction by gametogony & freshly passed oocyst is not infectious but it undergoes sporulation in the soil with the formation of 2 sporocysts, each containing 4 sporozoites. The one which sporulated oocyst is infective form.
The life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii
- Definitive host: Include cats & other felines (both sexual and asexual cycle)
- Intermediate host: Such as man and other different mammals (only asexual cycle).
- Intestinal phase – homologous host like cats
- Extraintestinal phase – heterologous host like a mouse, man, and other animals
- 2 types of life cycles:
- Enteric cycle
- Exoentric cycle
Clinical manifestation of Toxoplasma gondii
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease or abnormalities which is caused by the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii most often found in cats and farm animals.
Acute toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent host 80-90% asymptomatic, lymphadenopathy, fever, malaise, night sweats. Clinical manifestation of toxoplasmosis in AIDS, Brain involvement, focal CNS lesions, GI invasion.
Congenital toxoplasmosis has a severe neonatal disease, anemia, jaundice, mental retardation, seizures, visual defects, severe neurological sequelae, thrombocytopenia. Ocular toxoplasmosis has focal necrotizing retinitis.
Mode of infection
- Congenital
- Acquired
- Ingestion
- Inhalation
- Inoculation
- Blood transfusion
Lab diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii
Specimen collection
- Blood
- Bone marrow puncture
- Splenic puncture
- CSF
- Biopsy specimen ( Lymph node or muscle)
Microscopy
It is stained by Giemsa, PAS, or Gomori methenamine silver stain. The crescent-shaped Trachyzoites have seen in peripheral blood smear with blue cytoplasm and dark nucleus. Inoculation of sample in mice, guinea pigs, and hamsters
Serodiagnosis
- ELISA
- Indirect fluorescent antibody test
- Latex agglutination test
- Sabin–Feldman dye test
- It is the first serological test for toxoplasma antibodies to be described. The principle is the test is based on specific inhibition by antibody, of the staining of trophozoites by alkaline methylene blue.
- Skin test of Frenkel
- PCR
Treatment
Combined therapy with sulphonamide and pyrimethamine. Prednisolone used in ocular toxoplasmosis.
Prophylaxis
- Individuals at risk should avoid contact with cats and their feces.
- Avoid raw or semi-cooked meat.
- Proper washing of your hands also fruits and vegetables before eating.
- Blood or blood products or outcome should be screened for T.gondii antibody before transfusion
[embeddoc url=”https://notesmed.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Toxoplasma-gondii.pdf” download=”all” text=”Complete pdf file-Download”]