What is a lipoma?
Lipoma is a benign slow-growing painless tumor of adipocytes(adipose tissue), but angiolipoma is a variant of lipoma which is typically painful.
Lipomas are characteristically soft and lie more deeply in the skin (subcutaneous tissues) than epidermal tumors. It is the most common soft tissue tumor in adults.
What is inside a lipoma?
Lipomas are composed of lobules of mature adipose cells(Adipocytes) separated by delicate fibrous septa that have the same morphological structure as normal fat cells.
Angiolipomas have a vascular element and may be typically painful and tender in cold ambient temperatures.
These frequently require excision, when in fact other lipomas should be excised only when considered disfiguring.
Why do people get lipomas? (Causes of lipoma)
The exact causes of lipomas are unknown but some conditions may get lipomas. Lipomas are inherited tumors that pass down from one generation to the next.
You have a better chance to develop a lipoma if someone in your family has lipoma. Some diseases or conditions may cause lipoma;
- Gardner syndrome:
- It is also called familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) that is characterized by multiple colorectal polyps and other various types of tumors, both benign and malignant (cancerous) which may grow lipomas.
- Dercum’s disease:
- It is a rare disorder called adiposis dolorosa or Anders’ syndrome which causes painful lipomas to grow. It is most frequently seen on the arms, legs, and trunk.
- Hereditary multiple lipomatosis:
- It is also called familial multiple lipomatosis, this is a type of inheritance disorder (passed down from one generation to the next).
- Madelung’s disease:
- It is also known as multiple symmetric lipomatosis and occurs most frequently in men who excessively drink alcohol.
- Madelung’s disease may cause lipomas to grow and develop around the neck and shoulders region.
Types of lipoma
- Angiolipoma(fat and blood vessels). They are often painful.
- Conventional: The most common form of lipomas, in this lipoma, contains white fat cells. White fat cells store energy in the body.
- Fibrolipoma(Fat and fibrous tissue)
- Hibernoma (brown fat). Brown fat cells generate heat and help regulate and maintain body temperature.
- Myelolipoma(fat and tissues that produce blood cells).
- Spindle cell lipoma
- Pleomorphic (atypical): Various sizes and shapes of fat cells (adipocytes).
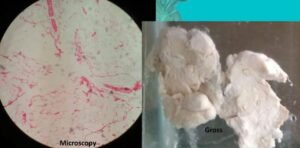
Morphology of lipoma
- Gross:
- Encapsulated, small, round to oval mass.
- Cut section: Soft, lobulated, yellowish-orange, and greasy tumors.
- Microscopy:
- It is composed of a large number of lobules of mature adipose cells which are separated by delicate fibrous septa. The lipoma is surrounded by a thin fibrous capsule.
Can lipoma grow fast?
Lipomas are benign (not cancerous) growth or tumors. In some cases, they can grow very rapidly and cause pressure on nearby tissues or organs in your body.
Lipomatous tumors are similar in nature to a common type of lump below the skin called lipomas.
Are lipomas dangerous?
Lipomas (skin lumpy mass) are classified as benign tumors or growth of fatty tissue. That means a lipoma isn’t cancerous so it is rarely harmful. The Treatment for lipoma normally isn’t necessary unless it’s bothering you.
Do lipomas hurt when pressed?
Lipomas are painless tumors that can be painful if they grow and press on nearby nerves or if they contain more blood vessels.
Do lipomas ever turn cancerous?
Lipomas are benign, not cancerous. Cancerous (malignant) tumors of the fat cells (adipocytes) are called liposarcomas. It is a very rare condition for lipomas to turn into a cancerous sarcoma (liposarcomas).
Do lipomas go away on their own?
Lipomas are benign growth or tumor masses which rarely go away on their own but also rarely cause problems. Sometimes plenty of patients have not wanted to have their lipomas eliminated. Lipomas cysts can become infected and have a chance to discharge completely. They can heal over with a scar but have a high probability of recurrence.
Do lipomas go away if you lose weight?
The lipoma cells (adipocytes) are believed to arise from primordial mesenchymal fatty tissue cells; thus, they are not of the adult type of fat cell origin.
They regularly increase in size with bodyweight gain, but interestingly, when losing your body weight usually does not decrease their sizes.
How can you tell the difference between lipoma and liposarcoma?
Lipoma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor and liposarcoma is a malignant (cancerous) mass. Lipoma tumors form just under the skin (subcutaneously), usually in the shoulders, neck region, trunk, or arms.
The mass tends to feel soft or rubbery and lobulated, yellowish-orange, and greasy mass moves when you push with your fingers.
While liposarcoma tumors form under deep tissue, the most common sites are the intermuscular region in the buttocks, thigh area, and retroperitoneum. They are circumscribed but infiltrating nodular mass.
Diagnosis of lipoma
- The best method of diagnosis of lipomas is the physical examination when a doctor or consultant asks if it is painful or tender.
- A biopsy is another method for the diagnosis of lipomas.
- When samples of the lipoma are sent to a lab for testing and that helps to diagnose the tumor.
- Imaging test: Ultrasonography, MRI, CT-scan
Treatment of lipoma
Should lipomas be removed?
No treatment is normally required in lipomas. However, if the lipoma bothers you, is painful, or has a growing mass then your doctor or consultant might recommend that it be removed surgically.
Lipoma removed by surgery which is a safe and effective method. An alternative method of lipoma surgery is liposuction to remove the lipoma.
Your doctor or consultant uses a long, thin needle to remove fatty tissue (adipose tissue) from the growing area.
How can I get rid of lipomas without surgery?
- Liposuction: It is also called vacuuming to remove the lipoma but generally doesn’t remove it all, however, the remainder grows back slowly.
- Steroid injection: This may shrink the lipoma but usually doesn’t fully work to remove the lipoma.
What is the best medicine for Lipoma?
Exact medicine is unknown for most tumors but in some conditions few drugs are available. So in this condition, the best method of treatment of lipomas are lipoma surgery, liposuction, and steroid injection.
How can I shrink my lipoma naturally?
Turmeric is called Curcumin which is a widely used spice in many households. It is an herbal remedy method that is known to be used for curing lipomas naturally.
Curcumin is an active ingredient which is found in turmeric plants that are known to help in the shrinkage of fatty lumps formed on the skin area.
What foods reduce lipomas?
Fish has good amounts of healthy fats called omega-3 fatty acids and good quality protein. Omega-3 fatty acids help to decrease inflammation of the body and may help to limit the growth of lipomas. Salmon and tuna fishes are excellent sources of omega-3-fatty acids as well as high in protein.
What type of doctor removes lipomas?
Dermatologists can remove lipomas if they continue growing or become bothersome. Dermatologists examine the lipoma and will decide how to remove it. The treatments include a simple procedure surgically removing the mass of the tumor.
What to do if a lipoma is painful?
They normally require no treatment other than observation by you and your doctor or consultant. However, if a lipoma is painful or continues to grow day by day it becomes a larger mass, so it can be removed by surgical procedure.
Although many lipomas don’t require any treatment, surgically removing them may be recommended for larger or painful ones.
Prevention of lipoma
Lipomas (and many of the other conditions that may cause lipomas) are generally inherited. Since they’re passed down into their families, it isn’t feasible to prevent them.
However, you can lower your risk of developing multiple symmetric lipomatosis (a condition that causes lipomas that chances to grow) by limiting the quantity of alcohol you drink.