What is Inguinal Hernia?
An inguinal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal contents (e.g. loops of the intestine) beyond the normal condition of the abdominal wall.
Clinically, the inguinal hernias appear as a pear-shaped swelling above the inguinal ligament, and above and medial to the pubic tubercle.
A hernia consists of three parts such as the hernial sac, contents of the sac, covering of the hernial sac. The hernial coverings are formed from the abdominal wall layers which pass through the hernial sac.
The inguinal hernias occur only in humans and not in other mammals due to evolutionary changes which have taken place in the inguinal region due to erect posture.
Types
There are two types of inguinal hernias that appear in the inguinal canal area, they are direct and indirect hernias.
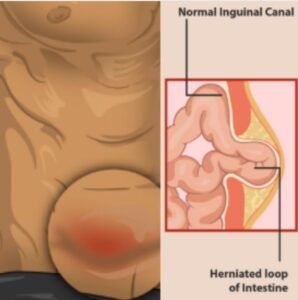
Indirect Inguinal Hernia
It is the most frequent form of inguinal hernia & believed to be congenital in origin. The hernia occurs if the hernia sac enters through the deep inguinal ring into the inguinal canal, lateral to the inferior epigastric vessel.
In this type of hernia, the predisposing factor is the complete or partial patency of the processus vaginalis. It may extend part of the way along with the canal or as far as the superficial inguinal ring present.
The hernia is complete when the processus vaginalis has undergone no obliteration, and It extends through the superficial inguinal ring down into the scrotum or labium majus.
Under these conditions, the neck of the hernial sac situated at the deep inguinal ring. It is twenty times more common in young males than females and it is more commonly present on the right side.
The indirect hernia may be acquired or congenital, they are briefly described below. If an internal ring occlusion test is done then the test should be positive.
Congenital indirect inguinal hernias
It mostly occurs due to patent processus vaginalis (an outpouching of the peritoneum), connecting the peritoneal cavity with the tunica vaginalis.
Acquired indirect inguinal hernias
It occurs due to increased intra-abdominal pressure during large weight lifting. When the intra-abdominal pressure is increased extremely, the abdominal viscera (abdominal contents) are pushed through the deep inguinal ring into the inguinal canal.
Direct Inguinal Hernia
It is globular in shape and extent rarely scrotal and it composes about 15% of all inguinal hernias. It is more common in old people mainly men with weak abdominal muscles and rare in women.
A hernial sac bulges forward through the posterior wall of the inguinal canal forward, medial to the inferior epigastric artery through the inguinal triangle(Hesselbach’s triangle).
The neck of the hernial sac is broad and the hernia leaves the triangle through its medial part or lateral part. The direct hernia is two types, they are; lateral direct hernia and medial direct inguinal hernia. If an internal ring occlusion test is done then the test should be negative.
Complete inguinal hernias
The term complete inguinal hernia is utilized if hernia contents reach the tunica vaginalis. If the hernia contents remain confined to the inguinal canal & don’t pass through the superficial inguinal ring it is called incomplete inguinal hernia & also called bubonocele.
Femoral hernia
It is less common in males but more common in females. The protrusion occurs into the femoral canal and the neck of protrusion of hernia lies below and lateral to the pubic tubercle.
Symptoms of hernia
In the hernia, exact symptoms are not found but some common symptoms are listed below
- A bulge in the area on either side of the pubic bone, which becomes more obvious when a person upright position, especially if straining or coughing.
- Burning or aching perception in the bulging area.
- Pain or discomfort in the groin region when people bending over, lift, or cough.
- Weakness or pressure in the groin region.
- Sometimes, pain and swelling around the testicles when the protruding intestine descends into the scrotum.
Causes of inguinal hernia
Actually, the causes of hernia are unknown but some conditions may cause the hernia, they are following condition may cause the hernia.
- Increased pressure within the abdominal region.
- Pregnancy:
- In this condition, pregnant women have weakened the abdominal muscles and increased the abdominal pressure inside the abdominal region that may cause a hernia.
- Chronic cough or sneezing may have high pressure in the hernial area that leads to causes a hernia.
- A preexisting weak spot in the abdominal wall area that leads to a hernia
- Straining during urination or bowel movement
- Strenuous(severe) activity may cause a hernia
- Abdominal muscles or wall weakness that may cause a hernia
Risk factors of hernia
- Male:
- Because the male testicle starts to develop inside the abdominal region and has to go down through an opening in the groin area to reach the scrotum (the sac that holds the testicles). If this opening does not close at birth, may chance to develop a hernia.
- Older people
- Weakness of strength of the abdominal wall and that conditions lead to increase intraabdominal pressure.
- White people
- Family history
- Chronic coughing for example smoking person.
- Chronic constipation condition
- Pregnancy because pregnant women have weakened the abdominal muscles and increased the abdominal pressure inside the abdominal region.
- Premature birth and low birth weight condition.
- Previous inguinal hernia or hernia repair condition.
Complications of hernia
- Incarcerated hernia
- Strangulation
- Pressure on the surrounding area
Prevention of hernia
- Maintain a normal healthy weight
- Emphasize high-fiber-rich foods and vegetables.
- Lift heavy objects carefully
- Avoid the heavy object lifting
- Cease the smoking.
Diagnosis
Physical examination should be done on hernial patients. Contact with consultant and consultant or doctor will check for a bulging area in the groin region.
In the standing and coughing condition, the hernia makes it more prominent and easy to study. Abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI should be done.
Treatment
The exact treatment is not found but the doctor or consultant might try applying the manual pressure to reduce the bulging before considering surgery.
Enlarging or painful hernias usually require surgery to relieve and prevent serious complications. There are mainly two types of hernia operations such as open hernia repair and minimally invasive hernia repair.