What is hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a clinical condition in which the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough crucial thyroid hormones. It may not cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages of the patients.
Over a long period of time, untreated hypothyroidism can cause various health abnormalities, such as myxedema in adults and cretinism in children, obesity, joint pain, infertility, and heart disease. Accurate thyroid function tests are available nowadays to diagnose hypothyroidism.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms are varied, depends on the severity of the hormone deficiency in patients. In the early stage, people may barely notice the symptoms of hypothyroidism, such as fatigue and weight gain or people feel getting older than the real age.
But as patient metabolism continues to slow, the patient may develop more severe problems. some common sign and symptoms include;
- Fatigue
- Increased sensitivity to cold
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Weight gain
- Puffy face
- Elevated blood cholesterol level
- Hoarseness
- Muscle weakness
- Muscle aches
- Tenderness, & stiffness
- Pain, stiffness, or swelling in your joints
- Heavier than normal or irregular menstrual periods
- Thinning of your hair
- Slowed heart rate
- Depression
- Impaired memory
- Enlarged thyroid gland (goiter)
When you have seen any of the above mention symptoms, then you start to consult your health care provider and start to treat this abnormality.
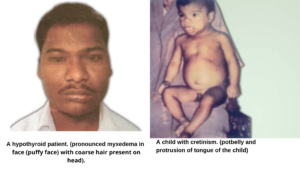

Hypothyroidism in Infants (Cretinism)
Hypothyroidism is most often affects middle-aged people and older women, anyone can develop the condition, including infants.
Initially seen, babies born without a thyroid gland or with thyroid gland but that does not work properly may have signs and symptoms.
Cretinism is hypothyroidism in infants, characterized by stunted growth.
When newborns children do have problems with hypothyroidism, the problems may arise that include:
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes is called Jaundice. In most cases, this occurs when a baby’s liver cannot work properly so cannot metabolize a substance called bilirubin, which normally forms when the body recycles old or damaged red blood cells.
- An enlarged, protruding tongue
- Difficulty in breathing
- Hoarse crying
- An umbilical hernia
- Failure of body growth and mental retardation
- Skeletal growth in a child is more inhibited than soft-tissue growth; so the child appears obese, stocky, and short appearance
- Constipation
- Poor muscle tone
- Excessive sleepiness.
When the initial stage of hypothyroidism in infants isn’t treated, even mild cases can lead to severe physical and mental retardation. When above mention symptoms appear in your child then consult your doctor to treat the symptoms and disease conditions.
Hypothyroid in adults (Myxedema)
It is hypothyroidism in adult people, characterized by generalized edematous appearance.
Causes for Myxedema
-
- Myxedema occurs due to thyroid gland diseases, genetic disorders, or iodine deficiency
- It is also caused by a deficiency of the hormone is called thyroid-stimulating hormone or thyrotropin-releasing hormone.
- A common cause of myxedema is the autoimmune disease called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, which is commonly seen in kate middle-aged women.
Signs and symptoms of myxedema
-
- Poor growth, resulting in short stature
- Delayed development of permanent teeth
- Delayed puberty
- Poor mental development
- Swelling of the face
- Bagginess under the eyes
- Non-pitting type of edema
- Atherosclerosis
Causes of hypothyroidism
The most common causes of hypothyroidism are the following;
- Autoimmune disease
It is the most common cause of hypothyroidism is an autoimmune disorder known as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
This disorder occurs when the human immune system produces a large number of antibodies that attack human own tissues and sometimes this process involves its own thyroid gland.
- Over-response to the treatment of hyperthyroidism
When people produce too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism) are often treated with radioactive iodine or anti-thyroid medications.
In this process sometimes, correcting hyperthyroidism can end up lowering thyroid hormone production too much, which results in permanent hypothyroidism.
- Thyroid surgery
Removing a large portion or all portion of the thyroid gland can diminish or halt hormone production.
- Radiation therapy
Radiation can be used in the treatment of cancer of the thyroid gland sometimes may lead to cause hypothyroidism.
- Medications
A number of antibiotics can contribute to hypothyroidism. For example, lithium is used to treat certain psychiatric disorders patients sometimes that lead to hypothyroidism.
Less common, hypothyroidism may result from one of the following abnormalities;
- Congenital disease
Some babies are born with a defective thyroid gland or absent of the thyroid gland.
- Pituitary disorder
It is a rare cause of hypothyroidism is the failure of the pituitary gland to produce enough thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). It is usually seen in benign tumors of the pituitary gland.
- Pregnancy
Sometimes, some women develop hypothyroidism during or after pregnancy (i.e. postpartum hypothyroidism), often because they produce large antibodies to their own thyroid gland.
If this condition is not treated that increases the risk of miscarriage, premature delivery, and preeclampsia.
- Iodine deficiency
Too little iodine can lead to cause hypothyroidism, and too much iodine worsens hypothyroidism.
Risk factors
- Women
- An older age than 60 years
- Have a family history of thyroid disease
- Have an autoimmune disorder, such as type-I diabetes or celiac disease
- Treatment with radiation through radioactive iodine or anti-thyroid medications
- Thyroid surgery (Partial thyroidectomy)
- Pregnant or delivered a baby within the previous six months.
Complications of hypothyroidism
If untreated hypothyroidism leads to a number of health problems appears such as,
Goiter
Sometimes, constant stimulation of the thyroid to release more hormones may cause the gland to become larger this is known as a goiter.
Heart problems
Hypothyroidism may also be associated with an increased risk of heart abnormalities such as heart disease and heart failure, primarily because of high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol i.e. the bad cholesterol can present in people with an unreactive thyroid.
Mental health problems
Depression may occur early stage of hypothyroidism and may become more severe after a long period of time. Hypothyroidism may also cause slow mental dysfunction.
Peripheral neuropathy
Long-term untreated hypothyroidism can cause damage or destruction to peripheral nerves in your body. These are the nerves that carry information (signal) from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of your body.
For example, people’s arms and legs. Peripheral neuropathy may cause pain, numbness, and tingling in the affected side.
Myxedema
This is a clinical condition, a life-threatening condition that is the result of long-term undiagnosed hypothyroidism.
The common sign and symptoms are presents include intense cold intolerance and drowsiness followed by profound lethargy and unconsciousness.
Infertility
A low level of thyroid hormone can interfere with ovulation, which impairs fertility.
Diagnosis of hypothyroidism
- Thyroid function test
Seen your serum TSH level and free thyroxine level. Serum TSH level, anti-thyroperoxidase, and antithyroglobulin antibodies are high in primary or low in secondary hypothyroidism and elevated in Hashimoto thyroiditis.
- Imaging test
Radiologic imaging tests are usually not necessary for patients with hypothyroidism. However, on CT Scan or MRI should be used.
Treatment of hypothyroidism
“Before the beginning of the thyroid hormone therapy, hypothyroid patients require at least a clinical assessment for adrenal inadequacy and angina”. The presence of either condition requires further evaluation and management.
Generally, synthetic levothyroxine is the preferred preparation for the treatment of hypothyroid patients. Sometimes, few clinicians prescribe mixtures of levothyroxine and triiodothyronine for hypothyroid patients. Monitoring the level of hormones in your body.
Prognosis
Patients with mild cases of hypothyroidism caused by Hashimoto thyroiditis have a remission rate of 11%. Hypothyroidism caused by interferon-alpha resolves within 17 months of stopping the drug in 50% of patients.
With levothyroxine treatment of hypothyroidism patients, striking transformations take place both in appearance and mental function in your body.
It is usually the rule to return to a normal state, but it will relapse if the treatment is interrupted. However, untreated patients with myxedema crisis have a mortality rate approaching 100%; even with optimal treatment, the mortality rate is 20–50%.
When to refer
- Difficulty titrating levothyroxine replacement to normal TSH level or clinically euthyroid state.
- Some patients with significant coronary artery disease needing levothyroxine therapy.
When to Admit
- Suspected myxedema crisis.
- Hypercapnia.