What is coronavirus?
A coronavirus is a large group of viruses which may cause illness in animals or humans being. In humans, several coronaviruses are known because of respiratory infections ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), and gastrointestinal abnormalities.
The most recently discovered coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) that causes coronavirus disease is called COVID-19.
Introduction
Coronaviruses belong to family Coronaviridae having two sub family i.e. Torovirinae and coronavirinae.
The former has been grouped into four genera such as; Alphacoronavirus, Betacorona virus, γ coronavirus, and delta coronavirus. Most of them infect the animal but gamma-coronavirus species which are pathogens in birds. Generally, human infection is uncommon but few species have adapted to human conditions.
Morphology
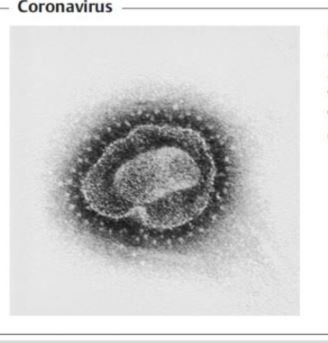
A coronavirus is a group of roughly spherical or pleomorphic linear, positive-senses sRNA of 26 to 32 kbp size and which is the largest among the non-segmented RNA viruses. It is pleomorphic due to the highly flexible envelop present.
Its carrying petal or club-shaped or crown-like appearance peplomer spikes that giving the appearance of the solar corona. Coronaviruses are large about (120-160 nm) size having helical symmetry.
Human coronavirus:
There are six recognized Coronaviruses that are known to cause human infections and most of them belong to Betacoronavirus but two recognized coronavirus i.e. Human coronavirus 228E and Human coronavirus NL63 that belongs to alphacoronavirus.
Six Human coronaviruses are listed below:
Alphacoronavirus;
- Human coronavirus 229E
- Human coronavirus NL63 (New haven coronavirus)
Betacoronavirus:
- Human coronavirus OC43
- Human coronavirus HKU1
- SARS-CoV (Severe Acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus)
- MERS-CoV (Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus)
- Recently pandemic virus; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) also known as novel human coronavirus 2019 (2019-nCoV)
Most of the coronaviruses are widely spread affecting people of most of the parts of the world and they mostly infect the upper respiratory tract and occasionally they cause diarrhea.
Mode of Transmission of coronavirus
Human coronaviruses propagate from person to person by coughing, sneezing, and close personal contact, such as touching mouth, nose, or eyes or shaking hands. And SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2) can also spread via droplets and rarely spread through the air (airborne) because of large size droplets.
Severe Acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV)
History
In November 2002, a new coronavirus emerged in the Guangdong province in China and, after originally being mistaken as a new influenza recombinant, was identified as the causative agent of a severe acute respiratory syndrome, or SARS, and in spring 2003 by WHO physician Dr. Carlo Urban and he diagnosed it in the businessman who had traveled from China, through Hong Kong, to Hanoi, Vietnam.
The doctor and the businessman whos first diagnosed with SARS but both died from an illness.
Epidemiology
During the 2003 outbreak, the SARS virus spread from Asia to the various regions of the world, and that cause within the months, more than 8000 patients worldwide affected and approximately 700 people died. And since 2004, there no case has been reported from anywhere in the world.
Source: SARS-CoV infection in humans believed to be contracted from different animals like monkeys, raccoon dogs, cats, Himalayan palm civets, and rodents.
Clinical manifestation
Respiratory symptoms mainly rapid onset of high fever, followed by a dry cough, dyspnea, and that leads to pneumonia. The severe respiratory syndrome followed an incubation period of approximately 2 to 7 days after the appearance of the initial symptoms i.e. severe lower respiratory tract infection; characterized by fever, headache, sore throat, myalgia, and malaise, etc.
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV):
It has caused a severe form of lower respiratory illness with a mortality of 30%.
Epidemiology
It was first reported in Saudi Arabia in 2012 after 10 years later from SARS-CoV.
Since that time, several hundreds of cases have been reported from various countries in the world mainly countries located in and around the Arabian Peninsula such as Saudi Arabia, UAE, Oman, Jorden, Qatar, Kuwait, Lebanon, and Iran.
Source
The source is unknown but it is believed to have been acquired from bats and camels.
People at increased high risk for MERS-CoV infection are:
- Recently they travel from Arabian Peninsula within 14 days
- Close contact with MERS confirmed the case.
- Healthcare personnel that they are not using any WHO-recommended infection control precautions(Standard precautions).
- People with exposure to infected bats and camels and other animals.
Clinical manifestation
- Incubation period: about 2-14 days
- Severe acute respiratory symptoms appear such as dry cough, high fever and shortness of breath (difficulty in breathing) may appear.
- Some people may develop gastrointestinal abnormalities such as diarrhea and nausea/ vomiting.
Complications
- Pneumonia and kidney failure mostly occur especially in people with underlying comorbid conditions.
COVID-19 (Novel coronavirus 2019-World Health Organization:
It is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) also called a Novel human coronavirus 2019 (2019-nCoV).
The novel human coronavirus 2019 (2019-nCoV) has the potential to be a global pandemic. Health officials announced it originated in Wuhan, China, in December 2019 that sold live and dead wild animals that people ate for food, improved health and vitality, and a number of other purposes.
The virus has now been detected globally; Australia, Canada, Finland, France, India, Italy, Japan, Nepal, Russia, Singapore, Spain, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam, the United States, and over a dozen other countries.
Incubation period: about 14 days
Symptoms of COVID-19
Most common symptoms:
- Fever
- Dry cough
- Tiredness
Less common symptoms:
- Aches and pains
- Nasal congestion
- Difficulty in breathing
- Headache
- Sore throat
- Conjunctivitis
- diarrhea
- Loss of taste or smell
- Rashes on skin
- Discoloration of finger or toes, etc.
These symptoms are generally mild and begin gradually changes. Some people become infected from this virus but only they have very mild symptoms.
Most of the people (about 80%) recover from the disease without needing any hospital treatment but require general human hygiene maintenance and nutrition.
Around 1 out of every 5 people who get COVID-19 becomes seriously ill and develop difficulty in breathing(shortness of breath).
And older people and people with underlying medical problems like heart and lung problems, high blood pressure(hypertension), diabetes, or cancer, are at higher risk of developing serious illness of COVID-19.
People of all ages who experience fever and/ or cough associated with difficulty breathing/shortness of breath(dyspnea), chest pain, or loss of speech or loss of movement should seek medical attention immediately.
Mode of transmission
Person to person transmission through small droplets from the nose or mouth, which are expelled when a person with COVID-19 coughs, sneezes or speaks. These droplets are relatively larger, do not travel far, and quickly sink to the ground.
People can easily catch COVID-19 if they breathe in these droplets(a large number of droplets) from a person infected with the virus. This is why it is important to stay at least a 1-meter distance away from another person.
These droplets can land on objects and surfaces around the person such as tables, toilets, beds, doorknobs, kitchen tables, and handrails.
People can become infected by touching these types of objects or surfaces, then touching their eyes, nose, or mouth. That is why it is important to wash your hands regularly with soap and water or clean with an alcohol-based hand rub.
Resistance
Studies have shown that the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) can survive for up to 72 hours on plastic and stainless steel, less than 4 hours on copper and less than 24 hours on cardboard these viruses survive.
As, always clean your hands with an alcohol-based hand rub or wash them with soap and water properly at least 20 seconds before touching your eye, nose, and mouth.
Lab diagnosis of coronavirus
Antigen detection
The Coronavirus antigens in the respiratory cells may be detected by the ELISA test and by using specific monoclonal antibodies.
Electron microscopy
It can be used to detect enteric coronaviruses from the stool.
RNA detection
- Real-time reverse-transcriptase Polymerase chain Reaction (rRT-PCR) assays are useful to detect coronavirus RNA in respiratory secretion and in stool samples and SARS-CoV RNA from the blood.
Isolation
Human coronaviruses in cell culture have been extremely difficult but one method i.e. traditional tracheal ring culture but no longer in use. SARS-CoV was isolated from the respiratory specimen using a Vero cell line.
Serum antibody detection
- ELISA and Hemagglutination inhibition tests are available for these viruses and a rising titer of antibody between acute and convalescent sera can be used to established diagnosis.
Treatment and prevention
- Still, there are no vaccines available and no specific drugs available for Coronaviruses infections.
Control measures are
- Isolation of patients (self-isolation)
- Quarantine of exposed people
- Travel restricted if needed
- Use WHO-recommended precautions such as; gloves, goggles, gowns, and respirators by healthcare workers.
- Avoids personal contact, i.e. sharing cups, or kissing, or eating utensils, shaking hands with infected people.
- Avoiding contact with infected camels, and other animals, uncooked milk, or meat.





