β-Oxidation fatty acids:
β-Oxidation of fatty acids may be defined as the oxidation of fatty acids on the β -carbon atom and results in the sequential removal of a two-carbon fragment, acetyl CoA.
It is a major pathway for the catabolism of fatty acids. Fatty acids oxidized by most of the tissues in the body and occur in the mitochondrial matrix. Brain, erythrocytes, & adrenal medulla cannot use fatty acids for energy requirements.
Stages of β-Oxidation fatty acids:
Involve three stages, they are;
- Activation of fatty acids occurring in the cytosol.
- Transport of fatty acids into mitochondria.
- β -Oxidation proper in the mitochondrial matrix.
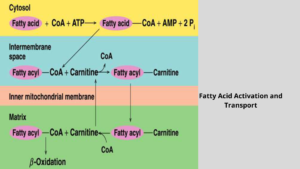
Fatty Acid Activation and Transport:
The fatty acid is converted into fatty acyl CoA which is the activated form by acyl CoA synthetase or thiokinases at cost of ATP.
Fatty acyl CoA combines with carnitine to form fatty acyl-carnitine (Carnitine transport system) by Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II.
Fatty acyl-carnitine transports the fatty acid into the matrix of the mitochondria. The fatty acyl-carnitine recombines with CoA for oxidation.
β -Oxidation proper in the mitochondrial matrix:
Inside the mitochondria, acyl CoA is sequentially dehydrogenated, hydrated, again dehydrogenated, and then cleaved to remove 2 carbon unit acetyl CoA.
Steps
- Oxidation/Dehydrogenation
- Hydration
- Oxidation
- Thiolysis (Cleavage).
Oxidation:
Acyl CoA undergoes dehydrogenation via. a FAD-depending on flavoenzyme, acyl CoA dehydrogenase, and a double bond is formed between α and β carbons.
Hydration:
Enoyl CoA hydratase carries regarding the hydration of the double bond to form β -hydroxy acyl CoA.
Oxidation:
β -Hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase catalyzes the second oxidation and generates NADH and β –ketoacyl CoA.
Cleavage:
The last reaction in β -oxidation is the release of a 2 carbon fragment, acetyl CoA from acyl CoA. It occurs by a thiolytic cleavage catalyzed by p-ketoacyl CoA thiolase (or simply thiolase).
The new acyl CoA, containing two carbons less than the original, re-enters the β -oxidation cycle. The process continues till the fatty acid is entirely oxidized. The overall reaction for each cycle of β-oxidation is,
Cn Acyl CoA + FAD + NAD+ + H2O + CoASH → C(n-2) Acyl CoA + Acetyl CoA + FADH2+NADH+H+.
Oxidation of palmitoyl CoA:
Palmitoyl CoA undergoes 7 cycles of β -oxidation to produce 8 acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA can enter the citric acid cycle and get completely oxidized to CO2 and H2O.
Palmitic Acid -ATP Synthesis:
- Palmitic Acid is C-16.
- Initiating Step -requires 2 ATP (activation step).
- Step 1 -FAD into ETC= 2 ATP.
- Step 3 -NAD+ into ETC= 3 ATP.
- Total ATP per circle of spiral = 5 ATP
- For example with Palmitic Acid compound= 16 carbons = 8 acetyl CoA
- Number of turns (circle) of fatty acid spiral = 7 turns
- ATP from fatty acid spiral (coiled) = 7 turns and 5 ATP per turn = 35 ATP.
- NET ATP from Fatty Acid Spiral (coiled) = 35 -2 = 33 ATP.
- Review ATP -Citric Acid Cycle or TCA cycle starts with Acetyl CoA
- NET=12 ATP per turn CITRIC ACID CYCLE.
- 8 Acetyl CoA = 8 turns CITRIC ACID CYCLE.
- 8 turns x 12 ATP/CITRIC ACID CYCLE=96 ATP.
- GRAND TOTAL(33+96) =129 ATP.
β -oxidation of odd chain Fatty acid:
The end outcomes are acetyl CoA & propionyl CoA. Propionyl CoA is first carboxylated using ATP and biotin to form D-methylmalonyl CoA. D-methylmalonyl CoA is converted into L-form by racemase. L-methylmalonyl CoA is then rearranged into succinyl CoA that enters the TCA cycle.
SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome):
Disorder due to blockade in β –oxidation caused by a deficiency in medium-chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD).
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) is an unexpected or unpredicted death of healthy infants, usually overnight. The cause is unknown. It is more prevalent than phenylketonuria.
Jamaican vomiting sickness:
It is characterized by severe hypoglycemia, vomiting, convulsions, coma, and death. It is caused due to eating unripe ackee fruit which contains an unusual toxic amino acid, hypoglycin A.
It inhibits the enzyme acyl CoA dehydrogenase, and thus β-oxidation of fatty acids is blocked, leading to various complications.
[embeddoc url=”https://notesmed.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Fatty-acid-oxidation.pdf” download=”all”]